(Bloomberg) — South African Mineral Resources Minister Gwede Mantashe issued a new Mining Charter last week, seeking to reduce uncertainty and boost investment in the sector.
The Background:
The set of rules, aimed at distributing the industry’s mineral wealth more equally among citizens after the injustices of apartheid, was first issued in 2004 and updated in 2010.
Previous Minister Mosebenzi Zwane published his own version last year, which was challenged in court by the industry. Mantashe, who was appointed in February and promised to consult everyone involved, issued an initial draft for comment in June. The Minerals Council South Africa, which represents most producers, says it’s studying the latest version.
Here are five key takeaways from the latest Mining Charter:
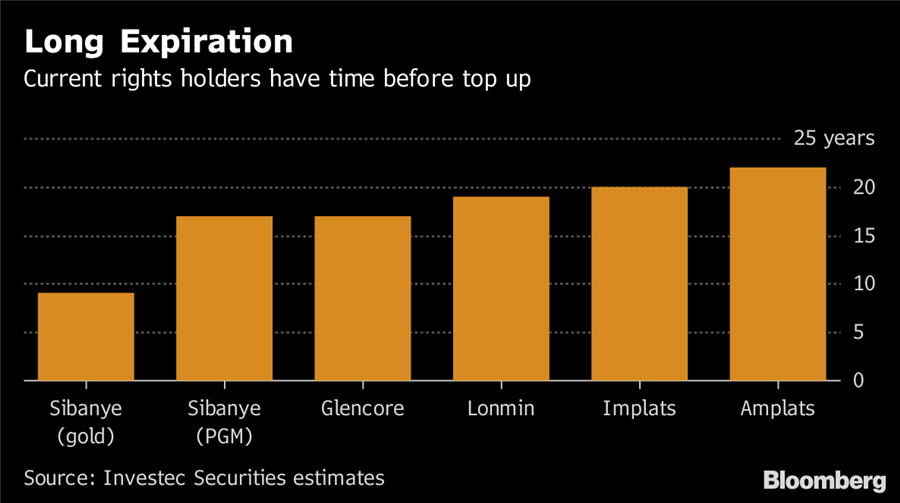
- Minimum Black Ownership (Existing Mine Rights) What happened before? The first two charters set it at 26%. Zwane wanted a top-up to 30% within one year, while Mantashe’s first draft said 30% in 5 years. New charter says: The minimum stays at 26% for the duration of existing mine right. (New mining right holders will need 30%.) This means: Mining companies that met the original requirements get to avoid diluting existing shareholders by being forced to add more black ownership.
- ‘Once Empowered, Always Empowered’ What happened before? There’s been an ongoing debate of whether previous black-empowerment transactions should be recognized even after the black shareholders exited. New charter says: The “recognition of continuing consequences” is clearly spelled out. This means: Companies that met the requirements previously won’t be forced to issue or sell new shares to black investors.
- Mine Right Renewal/Sale What happened before? Mantashe’s earlier draft said ‘once empowered, always empowered’ won’t apply if the mining right changes ownership or needs to be renewed. New charter says: That hasn’t changed. This means: Most companies won’t need to worry about renewal for several years. However, the ownership-change clause may restrict consolidation in the industry.
- Carried Interests (New Mining Rights) What happened before? Mantashe’s first draft required “free-carried interests” of 5% each for workers and community groups, which meant the respective groups wouldn’t have to buy their shares or pay their way. New charter says: The language has been changed to “carried interest,” and the charter says that the cost for the holding will be recovered by a right holder from development of the asset. Companies also have an option to pay an ‘equity-equivalent’ benefit to communities instead. This means: It’s still unclear, but analysts and lawyers have speculated mining companies can recover the value of the worker and employee stakes from the project’s profits, once it’s developed. That would make the requirement a lot easier to swallow.
- Dividends What happened before? Mantashe’s first version included a dividend equal to 1% of Ebitda for employees and communities. New charter says: The requirement appears to have disappeared. This means: Good news for mining companies, which have one less obligation to meet.
(By Paul Burkhardt)
The post South Africa’s latest mining charter: what’s new and who wins appeared first on MINING.com.
From:: Mining.com